Global Aircraft -- Alpha Jet
|
Aviation Center
US Attack
US Bombers
US Cargo
US Fighters
US Helicopters
US Patrol/Pursuit
US Reconnaissance
US Tankers
US Trainers
US UAV's
US X Planes
Orbiter Vehicles
WWI Aircraft
WWII Aircraft
Airbus
Antonov
Boeing
Dassault
Ilyushin
Kamov
MiG
Mil
Saab
Sukhoi
Tupolev
Yakovlev
Joint/Rest of World
Entertainment Center
Members Center
New Technologies
Contact Us
Extra Navigation
GAC Engine
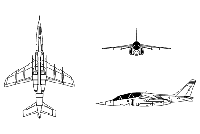
Alpha Jet Specifications
Alpha Jet Background
In the early 1960s, European air forces began to consider their requirements for the coming decades. One of the results was the emergence of a new generation of jet trainers to replace such classic aircraft as the Lockheed T-33 and Fouga Magister. The two main rivals in this exercise turned out to be the BAe Hawk and the Franco-German Dassault-Dornier Alpha Jet.
At the outset, the Alpha Jet had a lead, but the BAe Hawk would prove to be the winner in the race. However, the Alpha Jet has been built in good numbers and served with a number of air forces for several decades. In the early 1960s, the British and French began a collaboration on development of what was supposed to be a supersonic jet trainer/light attack aircraft. The result of this collaboration, the SEPECAT Jaguar, proved to be an excellent aircraft, but its definition had evolved in the interim, and the type emerged as a full-sized strike fighter, with two-seat variants used for operational conversion to the type. This left the original requirement unfulfilled and so the French began discussions with West Germany for collaboration. A joint specification was produced in 1968. The trainer was now subsonic, supersonic trainers having proven something of a dead end. A joint development and production agreement was signed in July 1969 which indicated that the two nations would buy 200 machines, each assembled in their own country. Proposals were generated by three groups of manufacturers: * Dassault, Breguet and Dornier submitted the "TA501", which had been developed through a merger of the Breguet 126 and Dornier P.375 concepts. * SNIAS/MBB submitted the "E.650 Eurotrainer". * VFW-Fokker submitted the "VFT-291". All the proposals were to be powered by twin SNECMA Turbomeca Larzac turbofans. The Luftwaffe had insisted that the trainer have two engines after suffering severe attrition from accidents with their single-engine Lockheed F-104 Starfighter. The Breguet-Dassault-Dornier TA501 was declared the winner of the competition in July 1970, with full development approved in February 1972. Two prototypes were to be built by Dassault in France (that company having bought out Breguet in the meantime) and two were to be built by Dornier in Germany. The first French prototype performed its first flight at Istres on 26 October 1973, with the first German prototype following from Oberpfaffenhofen on January 9 1974. The remaining two prototypes were in the air before the end of 1974. The French Air Force decided to use the Alpha Jet primarily as a trainer, and the first production Alpha Jet for the French performed its first flight on 4 November 1978. The French variant was known as the Alpha Jet E (the "E" standing for Ecole, French for "School") or Alpha Jet Advanced Trainer/Light Attack aircraft. Initial deliveries to France for service trials were in 1978, leading to introduction to line service in May 1979, replacing the Canadair T-33 in jet training and the Dassault Mystere IVA in weapons training. The Patrouille de France, air demonstration team of the French Air Force, fly the Alpha Jet. 176 production Alpha Jet E machines were delivered up to 1985, not the 200 that had been planned. The Luftwaffe decided to use the Alpha Jet in the light strike role, preferring to continue flight training in the sunny United States southwest on American trainer types instead of performing training in cloudy Germany. The first production German Alpha Jet performed its first flight on 12 April 1978. It was designated the Alpha Jet A (the "A" standing for Appui Tactique or "Tactical Strike") or Alpha Jet Close Support variant. The Luftwaffe obtained 175 machines up to 1983, with the type replacing the Fiat G91R/3. Manufacture of Alpha Jet subassemblies was divided between France and Germany, with plants in each country performing final assembly and checkout. The four prototypes remained in service as testbeds, for example evaluating a composite graphite-epoxy wing and improved Larzac engine variants. The different avionics fit makes French and German Alpha Jets easy to tell apart, with French machines featuring a rounded-off nose and German machines featuring a sharp, pointed nose. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||